What Is Knowledge Base Software? Everything You Must Know

Businesses today need knowledge-base software to manage and share information effectively. It helps reduce repeated customer questions by providing clear solutions in one central place. With an updated knowledge base, support teams save time and handle fewer tickets every day.
New employees can also learn faster by accessing detailed guides and tutorials. This software improves trust because customers know they can find accurate answers anytime. In short, knowledge base software cuts costs, saves time, and makes support more reliable.
What Is Knowledge Base Software?
Knowledge base software centralizes company information in a searchable, easy-to-use format. It organizes articles, FAQs, guides, and policies for quick access. Customers and teams find accurate answers without contacting support, reducing repeated questions and improving response consistency across channels.
How it works step by step
First, teams collect common questions and source documents to build articles. Next, editors write clear articles with short steps and real examples. Then, teams tag content and organise it into categories and topics. After that, articles with access controls are published and made searchable. Users search, browse, and find answers using keywords and helpful links. Finally, teams track views and feedback to update and improve articles regularly.
Common real-world examples
A product help center hosts manuals, setup guides, and troubleshooting steps. An employee intranet stores HR policies, training, and onboarding guides. IT teams keep troubleshooting steps, error fixes, and configuration notes handy. Sales and onboarding teams use cheat-sheets and short, quick-start checklists. Customer-facing FAQs let users solve billing and account issues themselves.
Also Read: New Software 418dsg7: The Future of Smart Technology Solutions
Core Functions of Knowledge Base Software
Organizing and storing company knowledge
Organize information into categories, topics, and clearly labelled articles for easy access. Use tags, folders, and version control to keep content tidy and updated. Set permissions so teams see onlythe relevant documents they need to use.
Search and navigation features
Provide fast, relevant search results with keyword, phrase, and filter support. Offer suggested articles, breadcrumbs, and clear menus to guide user journeys. Include innovative search features like synonyms and typo correction for accuracy. Ensure mobile-friendly navigation that works well on phones and tablets everywhere.
Content creation and editing tools
Provide a simple editor with templates, images, and rich formatting tools. Allow multiple authors, comments, and inline suggestions for collaborative editing. Use draft, review workflows, and publishing controls to ensure accuracy. Support templates and content blocks to speed article creation across teams.
Analytics and reporting functions
Track article views, search queries, and user feedback to measure usefulness. Identify content gaps and high-performing articles with clear, visual dashboards. Export reports to share insights with teams and improve support strategy. Use feedback and analytics to schedule regular updates and fix outdated content.
Businesses looking for more innovative solutions should read New Software RCSDASSK: Key Features, Benefits, and Business Impact for complete insights.
Different Types of Knowledge Base Software
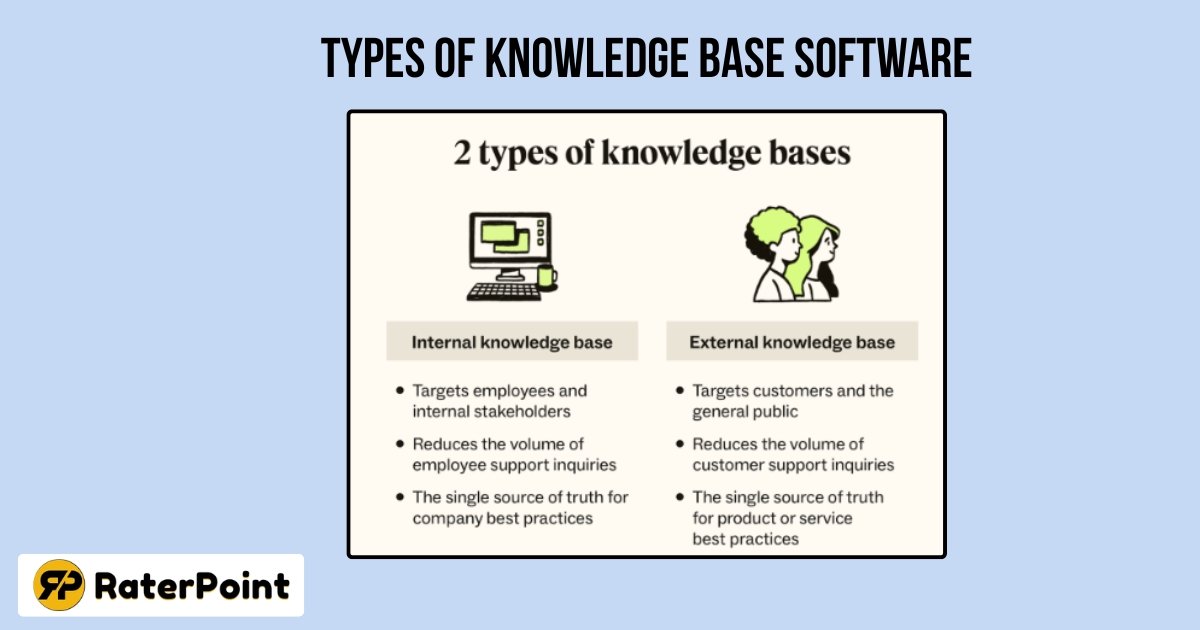
Internal knowledge base software (for teams)
Internal knowledge bases store procedures, policies, and team-specific documentation securely. They improve onboarding by quickly giving new hires clear, role-based guides. Admins set permissions so only the right teams can access sensitive articles. Typical uses include HR, IT, legal, and product support documentation.
External knowledge base software (for customers)
External knowledge bases publish help articles, FAQs, and product guides publicly. They reduce support tickets by letting customers self-serve simple issues instantly. SEO-friendly articles help users find answers through search engines and sites. Public feedback and ratings guide teams to improve documentation over time.
Hybrid solutions for enterprises
Hybrid knowledge bases combine internal and external content in one platform. They let companies share public help while restricting private notes. Granular controls manage who sees each article and which sections remain private. Enterprises often integrate hybrid systems with CRM and support tools for workflow. This approach scales documentation while effectively protecting sensitive company knowledge.
Must-Have Features in Knowledge Base Software
Easy-to-use editor
A simple editor helps authors write clear, consistent articles quickly. Templates, headings, and content blocks speed up article creation across teams. Media support and image uploads make steps easier for readers to follow. Drafts, autosave, and version history prevent accidental data loss or errors.
AI-powered search
AI-powered search returns relevant articles even when users type rough queries. It suggests articles, corrects typos, and understands synonyms for faster results. Search highlights let users jump to exact steps inside an article. Personalised results adapt to roles, permissions, and previous search behaviour.
Access control and permissions
Granular permissions ensure only authorized users view sensitive company documents. Role-based access simplifies managing who can edit or publish articles. Audit logs track changes, authors, and timestamps for accountability and compliance. Single sign-on and SAML support simplify secure team access management.
Multi-language support
Multi-language support lets teams publish articles in the customer’s native language. Automatic translation helps scale content but human review improves accuracy. Language fallback ensures users still see relevant help when translations are missing. Localization includes dates, currencies, terms, and examples for clear understanding.
Integrations with other business tools
Integrations connect the knowledge base with CRM, helpdesk, and collaboration tools. Embedding articles inside support tickets gives agents answers without leaving workflows. Syncing with product docs and changelogs keeps articles accurate after updates. APIs and webhooks allow automation and custom integrations for advanced workflows.
Benefits of Using Knowledge Base Software
Saves time and reduces support costs
A knowledge base lets customers find answers without contacting support. This reduces call volume and lowers overall support expenses quickly. Agents handle fewer simple queries and focus on complex issues. Automation and templates cut resolution time and increase first-response rates. Lower costs free budget for product improvements and team growth.
Improves customer experience
Clear, step-by-step guides and examples provide instant help. Consistent articles reduce confusion and improve product usability. Searchable content helps users find exact solutions without unnecessary steps. Feedback options let customers rate articles and suggest more straightforward explanations. Faster resolutions increase customer satisfaction and encourage more repeat business.
Enhances team productivity
Teams access standard procedures and reduce time spent reinventing solutions. Editors update articles quickly, so everyone uses the same accurate information. Shared templates and content blocks speed up article creation across departments. Search reduces time wasted looking for scattered documents and notes. Teams track knowledge gaps and prioritize updates with precise analytics.
Helps with onboarding and training
New hires learn faster using structured, easy-to-follow onboarding and reference guides. Training materials stay updated so employees consistently access current procedures. Interactive tutorials and checklists help learners practice key tasks confidently. Managers can assign learning paths and track completion with simple reports. Well-documented processes reduce errors and speed up team competency growth.
Best Practices for Setting Up a Knowledge Base
Choosing the right software
Pick a tool that matches your team size and workflow. Before buying, check features like search, editor, permissions, integrations, and analytics. I prefer a simple interface so authors can publish content quickly without confusion. Before buying, check security features, single sign-on, and data residency rules. Test the product with a short pilot before committing to a plan.
Structuring content for easy navigation
Create a clear hierarchy with categories, topics, and short article titles. Write concise headings and lead with the answer at the top. Use a table of contents and breadcrumbs to reduce user confusion. Add tags, related articles, and FAQs to improve search and discoverability. Keep content scannable with short paragraphs, bullets, and step lists.
Updating and maintaining articles
Set a regular review schedule to keep articles accurate and fresh. Assign owners who are responsible for updates and quality checks. Use version history and notes to track changes and reasons. Encourage feedback and ratings so users can highlight unclear content. Archive or delete outdated articles and redirect links to current pages.
Measuring success with analytics
Track metrics like article views, search terms, and average time on page. Monitor top search queries to find missing or poorly written articles. Measure resolution rate to see how often articles solve user problems. Use feedback scores and comments to prioritize content improvements quickly. Share regular reports with stakeholders to align knowledge goals and metrics.
Popular Knowledge Base Software Examples

Helpjuice
Helpjuice focuses on knowledge base performance and team collaboration for clarity. It offers powerful search, article analytics, and customizable templates for teams. Admins can easily set roles, control access, and brand the help center.
Zendesk
Zendesk provides a complete support suite with a strong knowledge base component. It connects tickets, live chat, and help articles for seamless agent workflows. Built-in analytics and automated suggestions help improve article usefulness over time.
Document360
Document360 targets technical documentation with a clean editor and versioning. It supports markdown, categories, and revision history for developer teams. Public portals and private projects help manage customer and internal docs separately.
Confluence
Confluence integrates tightly with Jira and other Atlassian collaboration tools. Its page hierarchy and macros let teams quickly build rich, linked documentation. Permissions and templates make it suitable for both small teams and enterprises.
Notion
Notion offers flexible pages that combine notes, databases, and embedded media. Teams can easily use Notion to build lightweight knowledge bases and internal wikis. Its simple sharing and templates make onboarding and quick references fast.
Knowledge Base Software vs. Document Storage Tools
Key differences explained
A knowledge base focuses on searchable, structured articles for quick answers. Document storage primarily holds files without an article-style structure or guided answers. Knowledge bases use templates, categories, and metadata to improve findability. Document tools rely on folders and filenames, making discovery harder at scale.
Search in a knowledge base ranks helpful articles and highlights exact steps. File storage search returns documents, but often misses specific in-article answers. To drive improvements, knowledge bases add user feedback, ratings, and article analytics. Document systems rarely include feedback or content performance metrics out of the box.
Why knowledge base tools offer more value
Knowledge base tools reduce support costs by enabling customer self-service every day. They speed resolution by surfacing exact steps and troubleshooting articles quickly. Teams avoid duplicated work through shared articles and standardized procedures across departments. Integrations with ticketing and CRM tools place answers directly inside agent workflows.
Analytics show content gaps and guide teams to update weak or missing articles. Structured content improves SEO so customers find help via search engines first. Permissions and access controls protect sensitive company knowledge while sharing public help. Overall, a knowledge base becomes a single source of truth for teams.
| Feature | Knowledge Base Software | Document Storage Tools |
| Purpose | Provide searchable articles and guided answers for customers and teams. | Store files, documents, and attachments without article-style organization by default. |
| Structure | Organizes content with categories, templates, tags, and interlinked articles for clarity. | Uses folders and subfolders with filenames to manage documents and files. |
| Search | Search returns relevant articles, highlights steps, and suggests related content. | Search finds files by name or content but lacks article-level precision. |
| Collaboration | Multiple authors edit articles with review workflows and version control for accuracy. | Share and edit files collaboratively, but often lack structured review workflows. |
| Analytics | Built-in analytics show article views, search terms, and user feedback clearly. | File systems rarely provide content performance metrics without extra tools added. |
| Integrations | Integrates with helpdesk, CRM, and chat for in-context answers and automation. | Integrations focus on file sync and backup with limited agent workflow support. |
| Best for | Customer support, onboarding, and shared team knowledge require quick answers. | Archiving, backups, ample file storage, and versioned document management are needed. |
Conclusion
Knowledge base software centralizes information for fast, searchable access across teams. It reduces support tickets by enabling self-service and straightforward steps. Teams save time using templates, search, and organized article libraries daily. Analytics and feedback help teams improve content and fix gaps quickly.
Choose software that matches your team size, budget, and workflow needs. Prioritize search quality, easy editing, permissions, and helpful decision-making analytics. Run a pilot to test usability and confirm it works with existing tools. Finally, commit to regular updates and clear ownership to keep content reliable.
FAQs on Knowledge Base Software
What is knowledge base software in simple terms?
Knowledge base software stores clear articles and answers for quick access. It helps people find accurate information without contacting support staff. Teams use it to share procedures, policies, and best practices easily. Users search, read steps, and solve problems without waiting for help.
What are examples of knowledge base tools?
Popular examples include Helpjuice, Zendesk, Document360, Confluence, and Notion today. Each tool offers different features for search, editing, and permissions. Choose a tool based on needs, budget, and team size. Try free trials to compare usability and core features quickly.
Which is the best platform for businesses?
The best platform depends on company size, workflow, and budget. Small teams may prefer Notion for simplicity and flexible pages. Enterprises often choose Confluence or Zendesk for scale and integrations. Test options with a short pilot before making a final decision.
Does Google have a knowledge management tool?
Google does not sell a single, dedicated knowledge base product for all teams. Teams often use Google Sites, Drive, and Cloud Search for simple knowledge needs. These tools lack built-in article templates, advanced analytics, and permissions for the KB. For full KB features, choose a dedicated knowledge base platform instead.
How does a knowledge base improve customer support?
A knowledge base gives customers instant answers to common problems and questions. It reduces ticket volume so agents focus on complex, high-value issues. Articles provide consistent steps, reducing errors and conflicting guidance between agents. Search analytics reveal missing topics, helping teams create more helpful content.

