Understanding Granular Recovery Technology | Best Practices and Backup Exec Integration

Data recovery refers to the process of restoring lost or deleted files from backups or storage systems. It plays a critical role in minimizing downtime and maintaining business continuity.
Granular Recovery Technology (GRT) allows organizations to recover specific items—such as individual emails or files—without restoring an entire backup. This targeted recovery saves time and reduces resource usage.
Backup Exec, a popular backup solution by Veritas (formerly Symantec), supports GRT across different environments, including virtual machines and Exchange servers. Following best practices ensures smoother operations, prevents errors, and improves recovery speed.
In this article, you’ll learn what GRT is, how it works with Backup Exec, common issues, and best practices for efficient data recovery.
What is Granular Recovery Technology?
Granular Recovery Technology (GRT) is a data recovery feature that allows you to restore individual items—like a single email, file, or database entry—without needing to recover the entire backup set. This method is faster, more efficient, and helps reduce downtime during data restoration.
It is especially useful in enterprise environments where quick access to specific data is critical. For example, if a user accidentally deletes one email, GRT can restore just that email instead of the full mailbox or server.
In simple terms, granular recovery technology offers precision-based data recovery tailored to the specific item or component you want to retrieve.
This approach answers the common question: what is granular recovery technology?
For more background, you can also check its summary listed on the granular recovery technology wiki, where the concept is defined in broader industry terms.
How GRT Differs from Traditional Recovery Methods
Below is a comparison table showing the key differences between Granular Recovery Technology and traditional recovery methods:
| Feature | Granular Recovery Technology (GRT) | Traditional Recovery Methods |
| Recovery Scope | Specific items (e.g., one email, file, or record) | Entire systems or full backups |
| Speed of Recovery | Fast, due to targeted recovery | Slower, requires restoring full backup sets |
| Storage Impact | Minimal | High, due to restoring unnecessary data |
| Ease of Use | User-friendly, with item-level browsing | More technical, manual work required |
| Resource Usage | Lower CPU and disk consumption | Higher resource demands |
| Common Use Case | Email, database, VM recovery | Full server or system recovery |
Common Use Cases
Granular Recovery Technology is widely used in various IT environments. Below are the most common and important use cases, explained simply:
1. Emails
GRT enables recovery of:
- Single or multiple emails
- Contacts and calendar entries
- Entire folders from Microsoft Exchange or similar platforms
This is particularly useful in legal and compliance scenarios where only one message may be needed.
2. Databases
GRT allows IT teams to:
- Restore individual tables or records
- Recover specific transactions
- Avoid full database restoration, saving time and resources
Common platforms include SQL Server and other enterprise-level databases.
3. Virtual Machines
Granular recovery supports:
- File-level recovery inside a virtual machine (VM)
- Restoring individual VMDKs or VM components
- Integration with hypervisors like VMware and Hyper-V
This reduces downtime in virtual environments and avoids unnecessary full VM recoveries.
How Granular Recovery Technology Works
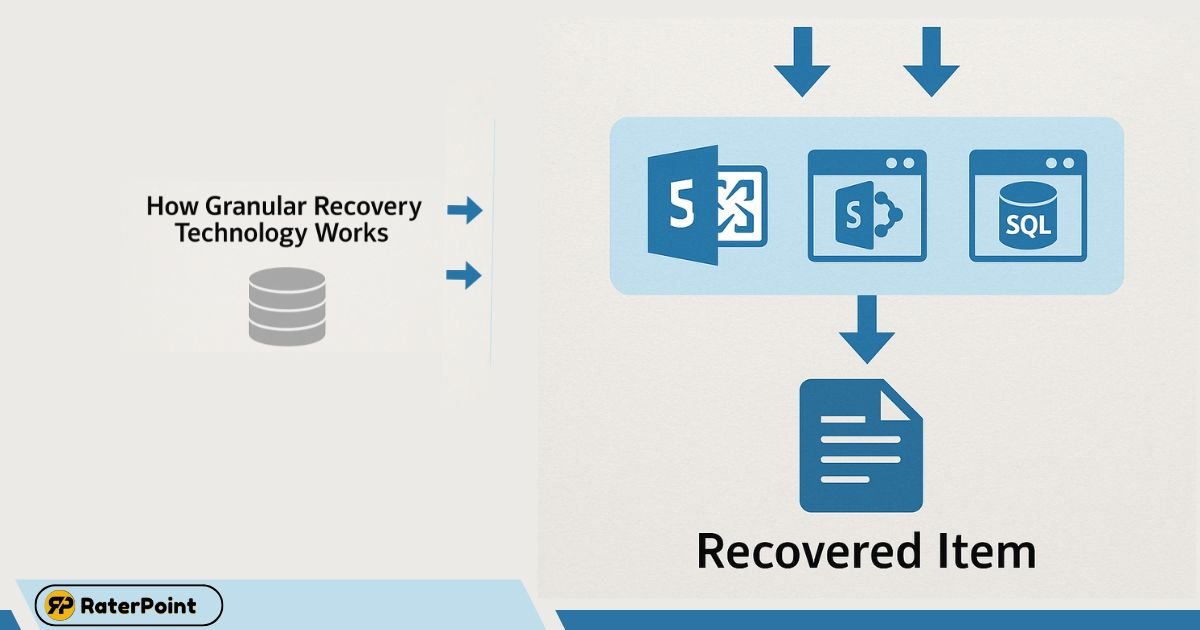
Step-by-Step: How GRT Functions
Granular Recovery Technology (GRT) works by indexing and cataloging the contents of a backup at a deeper level, allowing specific components—like a single file or email—to be restored without retrieving the entire backup set.
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how granular recovery technology GRT operates:
- Backup Process Begins
During a scheduled backup, GRT-enabled software (like Backup Exec) starts by creating a full backup of a system, application, or environment such as Exchange or SQL. - Granular Indexing
The software inspects the contents at the item level (files, folders, mail items, etc.). This process builds an internal index or catalog that stores detailed metadata about every item inside the backup. - Catalog Storage
The indexed data is stored separately, often in a catalog file or database, which allows users to browse and search backup contents later. - User Request for Recovery
When a user initiates a recovery, they don’t need to restore the full backup. Instead, they navigate the backup contents via the index and choose specific items. - Granular Restoration
Only the selected items are extracted from the backup image, making the process fast, lightweight, and targeted. - Post-Recovery Validation
Most systems run a check to verify the integrity and completeness of the restored item.
This detailed indexing and selection process is what allows precise control during granular recovery technology operations, resulting in minimal downtime and maximum efficiency.
Real-World Example: Recovering a Single Email
Imagine an IT administrator working in a mid-sized law firm. One of the senior partners accidentally deletes a critical email thread needed for a legal case. Rather than restoring the entire 50GB Exchange database, the admin uses GRT with Backup Exec.
Here’s what happens:
- They open Backup Exec, locate the specific Exchange backup from last week.
- Using the GRT interface, they browse through the mailbox content.
- The deleted email, identified by its subject and timestamp, is selected.
- In less than 2 minutes, the email is restored directly to the partner’s inbox—without interrupting the rest of the Exchange environment.
This kind of targeted recovery would not be possible (or would take hours) using traditional full restore methods.
File-Level vs Object-Level Recovery (Detailed Comparison)
Below is a deep comparison between file-level and object-level recovery, two core approaches in granular recovery technology:
| Feature | File-Level Recovery | Object-Level Recovery |
| Definition | Recovers individual files or folders from the file system | Recovers specific objects (e.g., email messages, DB rows, calendar) |
| Use Cases | Restoring documents, spreadsheets, images, etc. | Restoring mailbox items, SQL records, SharePoint objects |
| Indexing Depth | Based on file system and folder structure | Deep content-level indexing inside applications |
| Speed | Fast, depending on file size | Can be slightly slower due to complex object mapping |
| Supported Applications | Any OS-level or VM-level file systems | Exchange, SharePoint, SQL, Active Directory, etc. |
| User Access Needed? | Usually not, recovery is at the system level | Sometimes requires application-level permissions |
| Granularity | High, but limited to files | Very high, includes sub-components of applications |
| Examples | Recovering a PDF from a desktop folder | Recovering one calendar invite or a SQL table row |
While both methods serve unique needs, object-level recovery offers more precision for structured data within enterprise applications. File-level recovery is excellent for day-to-day file restoration in desktops or file servers.
Benefits of Using Granular Recovery Technology
Faster Data Restoration
Granular recovery technology enables quick restoration of specific data items without requiring the recovery of the entire database or system. This significantly reduces time spent on data retrieval, making it highly beneficial for addressing critical and time-sensitive data recovery needs.
Reduced Downtime and Operational Impact
By allowing the recovery of specific pieces of data instead of full system rollbacks, granular recovery minimizes the operational disruptions caused by recovery processes. Faster recovery translates to less downtime, ensuring business continuity and minimizing productivity losses.
More Control Over Specific Data Elements
This technology provides advanced precision by granting control over recovery operations at a granular level. It allows IT professionals to retrieve only the necessary files, emails, or records, eliminating the risk of overwriting or affecting other parts of the system during the recovery process.
To gain a broader understanding of how technology shapes modern workflows, you can explore What Is AV Technology, which highlights innovations in audiovisual systems and their impact on efficiency and precision in various sectors.
Cost-Effectiveness in Enterprise Environments
Granular recovery minimizes the costs associated with full-scale data recovery operations by reducing resource usage, time expenditure, and potential revenue loss caused by downtime. It is an efficient solution for enterprises aiming to manage recovery processes while keeping expenses under control.
Backup Exec and Granular Recovery Technology Integration
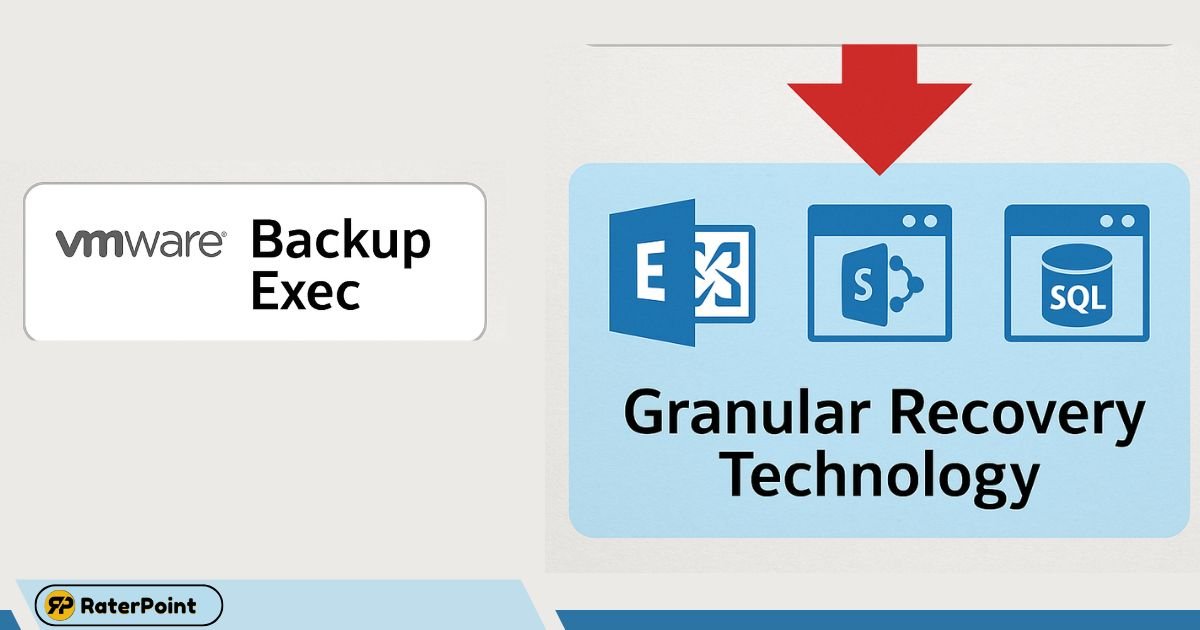
What is Backup Exec?
Backup Exec is a robust data protection and recovery software designed to simplify and streamline the backup and restoration process for businesses of all sizes.
Developed initially by Veritas (previously Symantec), Backup Exec offers reliable and high-performance solutions that cater to both physical and virtual environments. One of its standout features is the integration of Granular Recovery Technology (GRT), which allows for efficient and precise data recovery.
How it supports granular recovery:
Granular Recovery Technology enables users to perform highly targeted recovery, such as individual items instead of entire systems or databases. For example, granular recovery technology in Exchange 2013 environments allows administrators to recover specific emails, mailboxes, or attachments directly from backups without the need for a full restoration.
This capability not only saves time but also reduces storage and resource requirements, making it a valuable tool for enterprise-grade data management.
Specific versions (2010, 2012, 2014, 2015):
Over the years, Backup Exec has evolved to enhance its GRT capabilities:
- Backup Exec 2010: Marked significant advancements in GRT, making it easier to recover items from Microsoft Exchange and SharePoint. It supported seamless integration with virtual machines.
- Backup Exec 2012: Focused on simplifying backup workflows while maintaining robust GRT performance, particularly with virtualized environments.
- Backup Exec 2014: Introduced enhanced compatibility with newer platforms and streamlined granular recovery technology for Exchange 2013 and SharePoint.
- Backup Exec 2015: Adapted to modern demands, improving performance with virtual machines and providing quicker restoration times, solidifying its stance as a leading recovery solution.
Compatibility with virtual machines and Exchange:
Backup Exec is fully compatible with virtual machines, including VMware and Hyper-V, providing support for single-pass backups with GRT. This allows businesses to back up entire virtual environments while maintaining the ability to recover individual files or items within a virtual machine.
Similarly, its integration with Microsoft Exchange, including Exchange 2013, ensures that users can recover specific mail items directly from backups created with Backup Exec granular recovery technology. The seamless compatibility across platforms makes it an ideal choice for diverse IT infrastructures.
Backup Exec’s granular recovery solutions are indispensable for organizations, allowing precise and efficient data recovery from both virtual and physical systems.
By integrating Symantec Granular Recovery Technology and maintaining backward compatibility, this tool ensures reduced downtime and enhanced business continuity in today’s complex data environments.
To further understand the role of connectivity in such advancements, you can explore What Is Network Technology, which dives into the critical infrastructure enabling seamless communication and data exchange across systems.
Best Practices for Using Granular Recovery Technology

To make the most of Backup Exec’s granular recovery technology, it’s essential to follow best practices that enhance efficiency and reliability.
Below are detailed, easy-to-understand guidelines for each aspect:
Backup Scheduling Tips
Plan your backup schedules carefully to minimize disruptions and ensure consistent data protection.
It’s a best practice to perform full backups during low-usage times, such as after business hours, and use incremental or differential backups daily to reduce backup time and storage requirements. Regular scheduling ensures you always have recent recovery points available.
Storage Configuration for Optimal Performance
Proper storage configuration is critical for efficient backup and recovery operations. Use high-speed storage solutions like SSDs or dedicated NAS devices for storing backup files.
Also, ensure that your storage media has sufficient capacity to handle both the backup data and future growth.
Avoid storing backups on the same physical location as the primary data to protect against hardware failures or disasters.
Recommendations for Different Backup Exec Versions
Each version of Backup Exec may offer unique features and enhancements, so it is important to review the specific functionalities of your version.
Keep your Backup Exec software updated to access the latest features and security updates. If using older versions, confirm compatibility with your operating systems and hardware, and consider upgrading if essential features are unavailable.
Data Validation and Test Recovery Drills
To ensure your backups are reliable in case of an emergency, perform regular data validation and recovery tests. Validation checks ensure the data in your backups is not corrupted, while test recovery drills verify that the restoration process works as intended.
These practices help identify issues before they become critical problems and build confidence in your recovery plan.
By following these best practices, you can fully leverage granular recovery technology to protect your organization’s vital data and ensure business continuity in both virtual and physical environments.
Read More: Wepbound: Why Everyone in Tech Is Talking About It
Granular Recovery with SQL and Exchange
Granular Recovery Technology (GRT) is an advanced tool that simplifies the recovery of specific data points in SQL databases and Exchange environments without restoring entire backups. This functionality is especially useful in critical scenarios where quick, targeted data recovery is essential.
How GRT Works with SQL Databases
Granular recovery technology for SQL allows users to locate and retrieve individual tables or records directly from a backup. Instead of performing full database restores, this method minimizes downtime and ensures faster access to the required information. It is particularly beneficial when responding to database corruption or accidental deletions.
Recovery of Mailbox Items from Exchange 2013
Using granular recovery technology with Exchange 2013, administrators can restore individual mailbox items such as emails, calendar events, or contacts. This precise recovery capability eliminates the need to restore entire mailboxes or databases, saving both time and storage resources.
Limitations and Supported Configurations
While granular recovery technology with SQL and Exchange 2013 offers significant advantages, it is essential to understand its limitations. Some advanced configurations or encrypted backups may require additional steps for successful recovery.
Additionally, ensuring compatibility between the backup software and server environments is critical for seamless operation. Proper planning and regular validation are recommended to maximize the efficiency of GRT.
By leveraging granular recovery technology for SQL and Exchange 2013, organizations can achieve quicker recovery times and reduce disruption to operations.
Future Trends in Granular Recovery Technology

IT Disaster Recovery Plans
IT disaster recovery plans are essential for ensuring that an organization can quickly respond to and recover from unexpected disruptions, such as hardware failures, cyberattacks, or natural disasters.
These plans outline a structured approach to restore critical IT systems and minimize downtime, helping to protect business operations and reduce potential losses. Key components of an effective
IT disaster recovery plan include identifying critical systems, creating data backup strategies, defining recovery objectives, and regularly testing the plan to ensure its effectiveness.
By having a well-prepared disaster recovery plan in place, organizations can maintain operational resilience and safeguard their data and infrastructure.
Advances in backup and recovery solutions
Advances in backup and recovery solutions have significantly enhanced the ability of organizations to safeguard their critical data and systems. Modern solutions often feature automated backup processes, reducing the risk of human error and ensuring data is consistently protected.
Cloud-based technologies now allow businesses to store data securely offsite, offering flexibility and faster recovery times in case of a disaster. Additionally, advancements in backup solutions include features such as real-time backups, incremental snapshots, and artificial intelligence to predict and prevent potential failures.
These innovations not only improve the speed and efficiency of recovery but also provide businesses with greater confidence in maintaining continuity during unexpected events.
Role of Cloud Storage and Hybrid Systems in Data Recovery
Cloud storage plays a vital role in modern data recovery strategies. It allows businesses to back up their critical data safely in remote servers, making it easily accessible during emergencies. With cloud storage, files and systems can be restored quickly, minimizing downtime and ensuring smooth operations.
Hybrid systems, which combine on-premise storage with cloud solutions, offer even greater flexibility and reliability. They allow businesses to store frequently used data locally for faster access, while simultaneously backing up crucial data in the cloud.
This combination ensures that even if one system fails, data is still protected and recoverable from the other source. By using cloud storage and hybrid systems, businesses can achieve a balanced and efficient approach to safeguarding their data.
Expectations for Handling Growing Data Environments
Managing growing data environments requires careful planning and effective strategies to ensure stability and scalability. Businesses should expect to implement systems that can adapt to increasing data volumes without compromising performance.
It is essential to prioritize data organization and establish clear protocols for categorizing and storing information efficiently. Regularly updating infrastructure and integrating advanced technologies, such as automation and artificial intelligence, can help streamline data management processes.
Additionally, consistent monitoring and proactive maintenance are crucial to prevent bottlenecks and address potential issues before they escalate. By focusing on flexibility, security, and reliability, organizations can successfully handle the challenges of expanding data environments while supporting their operational needs.
FAQs
What is granular level recovery?
Granular level recovery refers to the ability to recover specific pieces of data, such as files, folders, emails, or databases, instead of restoring an entire backup. This approach ensures efficiency by retrieving only what is needed.
Is granular recovery available for virtual machines?
Yes, granular recovery is available for virtual machines. Many modern backup solutions support this feature, allowing users to recover individual files or applications from virtual machine backups without restoring the entire VM.
What is a granular restore?
A granular restore is the process of recovering specific data elements from a backup rather than performing a full recovery. This allows organizations to save time and resources by focusing on retrieving only the necessary components.
What are the types of backup granularity?
Backup granularity typically includes full backups, incremental backups, differential backups, and object-level (or granular) backups. Each type serves different purposes depending on the level of detail and recovery speed needed.
What is GRT in Backup Exec?
GRT, or Granular Recovery Technology, in Backup Exec is a feature that enables users to recover individual items, such as emails from an Exchange database or files from a virtual machine, directly from the backup.
What is granular in technology?
Granular in technology refers to a high level of detail or specificity. For instance, granular recovery involves precise actions, like recovering individual files or data points, as opposed to broader system-wide processes.
What is an example of a granular level?
An example of a granular level in recovery would be retrieving a single deleted email from a backed-up mailbox instead of restoring the entire email server. This precise recovery method showcases how granular solutions can address specific needs effectively.
Conclusion
Integrating Granular Recovery Technology (GRT) with Backup Exec offers numerous benefits, including enhanced data management efficiency, improved scalability, and fortified security. These advantages empower organizations to effectively handle the growing demands of modern data environments while ensuring that their critical information remains accessible and protected.
However, it is essential to carefully consider factors such as infrastructure updates, automation, and the implementation of best practices to maximize these benefits. Consistent monitoring and proactive maintenance are key to successfully addressing challenges and avoiding potential disruptions.
By adopting GRT and Backup Exec in tandem and adhering to industry-recommended standards, organizations can create a robust and flexible framework that meets their operational needs while paving the way for long-term success. Taking these steps ensures reliable data protection and positions businesses to thrive in an increasingly data-driven world.
Additional Resources
References to Backup Exec support tools and resources
https://www.veritas.com/support/en_US/dpp.BackupExec
Further reading on data recovery technologies:

